In an era where roads are busier than ever, car accidents remain a leading cause of injury and death worldwide. As of 2025, motor vehicle crashes continue to claim lives at an alarming rate, with the World Health Organization reporting that road traffic injuries account for about 2.37% of global deaths, making them the eighth leading cause overall. In the United States alone, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) estimates that over 2 million people are injured in traffic accidents annually, with fatalities hovering around 40,000 per year despite advancements in technology. These statistics underscore a harsh reality: while vehicles have become smarter and safer, human error and preventable oversights still fuel most incidents. But there’s good news. Proven injury prevention techniques can dramatically reduce risks. This blog dives deep into practical strategies, backed by the latest guidelines and data, to help you and your loved ones stay protected on the road.
Whether you’re a daily commuter, a parent shuttling kids, or someone planning a long road trip, understanding these techniques isn’t just about compliance; it’s about survival. From buckling up correctly to leveraging cutting-edge vehicle tech, we’ll explore how small habits and smart choices can make a massive difference. Let’s break it down step by step, starting with the basics and moving into advanced protections.
The Foundation of Safety: Proper Seat Belt Usage
Seat belts are often called the “simplest and most effective” tool for preventing injuries in car accidents, and for good reason. According to recent data, wearing a seat belt in the front seat reduces the risk of death by 45% and serious injuries by 50%. In rear seats, the figures are even more compelling, with a 25% reduction in fatalities when belts are used properly. Yet, misuse remains common. Belts worn too high on the abdomen or loose across the shoulder can cause internal injuries during a crash.
To use a seat belt correctly, ensure the lap portion sits low across your hips, not your stomach, to anchor you firmly without risking organ damage. The shoulder strap should cross your chest and collarbone, avoiding the neck or slipping off the shoulder. For pregnant women, position the lap belt under the belly and the shoulder belt between the breasts. Always adjust for a snug fit; any slack reduces effectiveness.
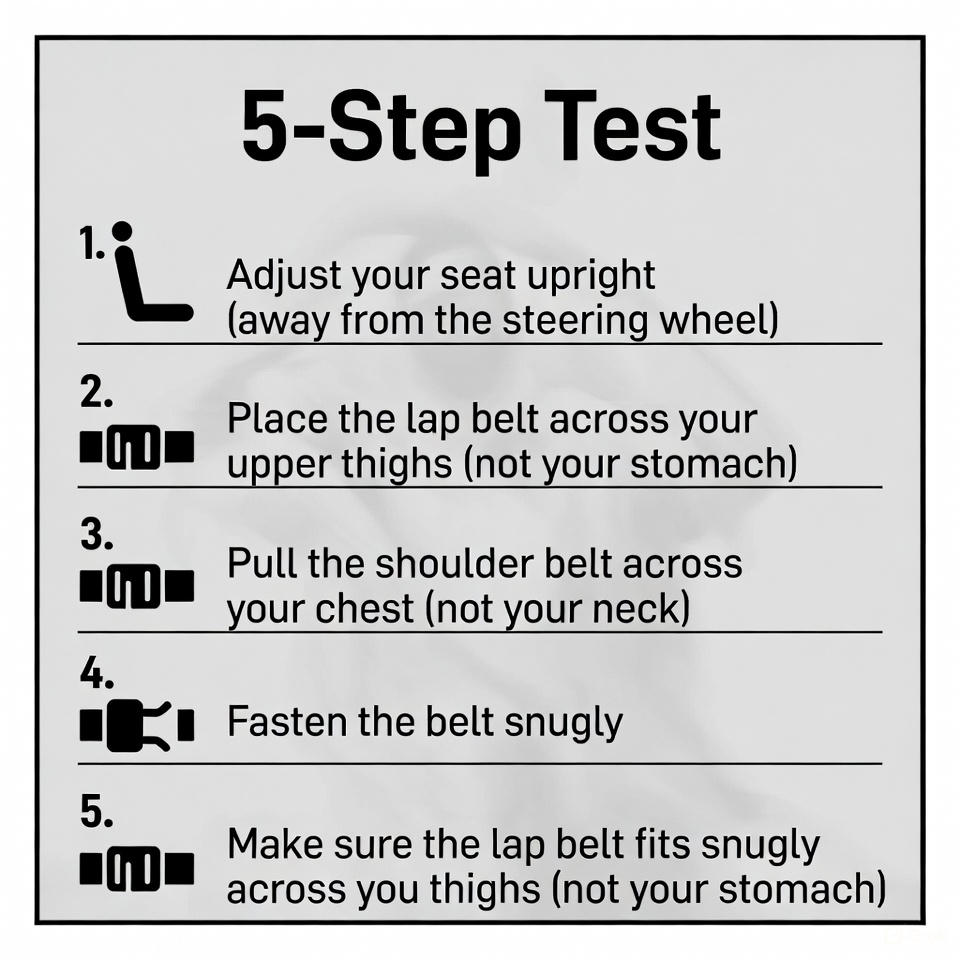
Children and shorter adults may need boosters to achieve the right fit. The NHTSA’s “5-Step Test” is a handy guide: the belt should touch the thighs, not the stomach; the shoulder strap should hit mid-chest; and the child should sit all the way back with knees bending naturally over the seat edge. Ignoring these can lead to “seat belt syndrome,” where improper use causes spinal or abdominal injuries. In 2025, with more vehicles featuring automatic tensioners, double-check that your belt locks in a crash simulation mode if available.
Education plays a key role here. Campaigns like those from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasize that seat belts save an estimated 15,000 lives yearly in the U.S. alone. If everyone buckled up, we could prevent thousands more injuries. Remember, it’s not just about you. Unbelted passengers can become projectiles in a collision, endangering others.
Protecting the Youngest Passengers: Child Safety Seats
When it comes to children, standard seat belts aren’t enough. Child safety seats reduce the risk of death by 71% for infants and 54% for toddlers in passenger vehicles. With road traffic injuries being a top killer for kids aged 5-14 globally, proper installation and use are non-negotiable.
Start with rear-facing seats for infants up to at least age 2, or until they outgrow the height/weight limits. These provide crucial neck and spine support in frontal crashes, which account for over 50% of accidents. Transition to forward-facing harness seats, then boosters, keeping kids in each stage as long as possible. By 2025, many states mandate boosters until age 8 or 4’9″ tall, aligning with NHTSA recommendations.
Installation is where many falter. Up to 75% of seats are misused. Use the Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children (LATCH) system for a secure fit, but don’t exceed weight limits (usually 40-65 lbs combined). If using a seat belt, ensure it’s locked and threaded correctly. Get a free inspection at certified stations; the NHTSA reports that professional checks fix 90% of errors.
Never place rear-facing seats in front of active airbags, and avoid aftermarket add-ons that aren’t crash-tested. For older kids, teach them to buckle independently, but supervise until habits stick. In multi-child families, consider vehicle seating. The middle rear is safest for one seat. These measures aren’t just rules; they’re lifesavers, as evidenced by a 50% drop in child fatalities since widespread adoption began.
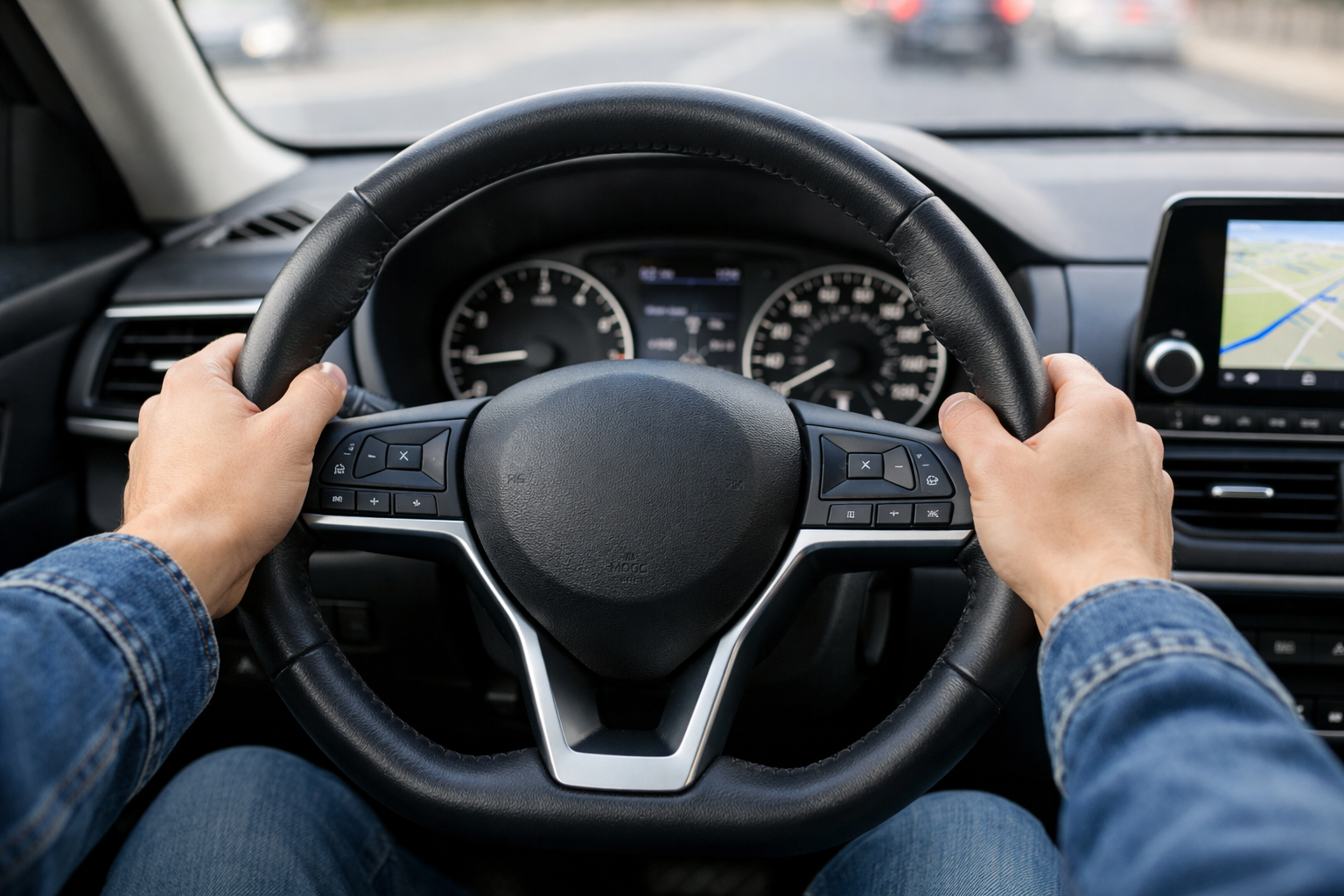
Optimizing Your Driving Position for Maximum Protection
Your posture behind the wheel isn’t just about comfort. It’s a critical injury prevention factor. Sitting too close to the steering wheel increases airbag injury risk, while poor hand placement can lead to arm fractures or loss of control.
The ideal position: Sit upright with at least 10 inches between your chest and the steering wheel to allow safe airbag deployment. Adjust the seat height so your eyes are level with the top third of the windshield, ensuring clear visibility. Feet should reach pedals without straining, and the headrest should align with the back of your head to prevent whiplash.
For hands, the 9 and 3 o’clock positions are recommended in 2025 guidelines, replacing the outdated 10 and 2 due to airbag concerns. This grip offers better leverage for evasive maneuvers and keeps arms safe from deploying bags. Use hand-over-hand steering for turns to maintain control.
Pregnant drivers should tilt the wheel toward the chest, not belly, and consult doctors for extended drives. These adjustments reduce injury severity by distributing crash forces evenly, per IIHS studies.
Leveraging Passive Safety Features: Airbags and Beyond
Airbags have saved over 50,000 lives since 1987, but they’re supplements, not replacements, for belts. Frontal airbags deploy at speeds over 10-15 mph in crashes, inflating in milliseconds to cushion impacts. Side, curtain, and knee airbags add layers, reducing head injuries by 60% in side collisions.
However, improper use can harm. Children under 13 should ride in back to avoid frontal airbag force. In 2025, smart airbags with sensors adjust deployment based on occupant size and position, minimizing risks.
Other passives include crumple zones, which absorb energy, and reinforced cabins. Always ensure airbags are active unless medically exempted.
Embracing Active Safety Technologies in Modern Vehicles
2025 vehicles boast advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that prevent crashes altogether. Automatic emergency braking (AEB) stops or slows the car if a collision is imminent, reducing rear-end crashes by 50%. Lane-keeping assist and blind-spot monitoring alert or correct drifts, while adaptive cruise control maintains safe distances.
Electronic stability control (ESC), mandatory since 2012, prevents skids and rollovers, cutting single-vehicle fatalities by 30-50%. The NHTSA’s 2025 progress report highlights these in their National Roadway Safety Strategy, aiming for zero deaths.
When buying, check IIHS Top Safety Pick ratings. Vehicles with these features score highest in crash tests.
Cultivating Safe Driving Habits to Avoid Accidents
Prevention starts with behavior. Distracted driving causes 25% of crashes; put phones away. Texting multiplies risk by 23 times. Follow the three-second rule for following distance, adding time in bad weather.
Avoid impairment: Alcohol contributes to 30% of fatalities. Defensive driving. Scanning ahead, anticipating errors. Saves lives. The CDC promotes interventions like sobriety checkpoints.
Speeding exacerbates injuries; obey limits. Fatigue mimics impairment. Rest every two hours on long trips.
The Role of Vehicle Maintenance in Injury Prevention
A well-maintained car is safer. Check tires monthly. Underinflation causes 11,000 crashes yearly. Brakes, lights, and fluids prevent failures. In 2025, smart diagnostics in EVs alert to issues early.
Regular servicing aligns with NHTSA’s tips for safe driving resolutions.
Choosing and Upgrading for Safety
Opt for vehicles with high safety ratings. Features like pedestrian detection are standard in many 2025 models. Retrofitting older cars with dash cams or aftermarket AEB adds protection.
Wrapping Up: A Commitment to Safer Roads
Injury prevention in car accidents boils down to preparation, awareness, and action. By adopting these techniques. From buckling up to embracing tech. You’re not just protecting yourself but contributing to global goals like halving road deaths by 2030. As the 2025 Roadmap to Safety emphasizes, community efforts amplify individual ones. Drive safe, stay informed, and remember: every trip is a chance to arrive alive.